MinuteTM Total Protein Extraction Kit for Adipose Tissues/Cultured Adipocytes (20 Tests)
Manual/protocol
MSDS sheet
Adipose tissue, especially white adipose tissue (WAT), has been recognized as an important endocrine and inflammation organ in addition to its energy storage function. Isolation and analysis of proteins from adipose tissues are increasingly critical for understanding many physiological/pathological conditions. However, isolation and analysis of WAT and brown adipose tissue (BAT) are technically very challenging due to their high lipid and low protein contents. The water-oil emulsion present in biological sample is notoriously difficult to separate. We have developed a novel technology to address this issue. A porous filter with unique surface property and pre-defined pore size and thickness coupling with a specially formulated detergent-free extraction buffer is employed to rapidly and effective separate water-oil emulsion derived from adipose tissue homogenate. The extraction buffer has lower freezing point than that of oil in adipose tissues and the aqueous phase can be quickly separated from oil phase by passing the tissue homogenate through the filter. The total proteins isolated are un-biased representation of cellular proteins in the tissue. The extracted proteins concentration is very high (2-3 mg/ml) as compared to other methods.

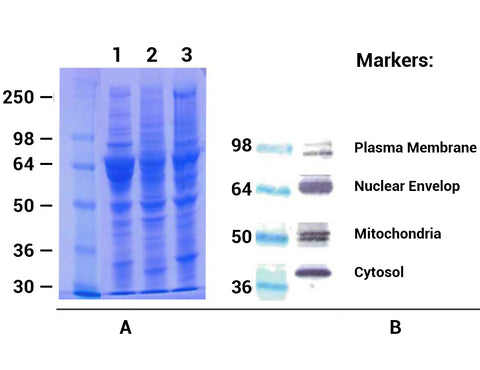
A. SDS-PAGE (10%) profiles of total protein extracted from different adipose tissues. Lane 1, porcine WAT; Lane 2, chicken BAT; Lane 3, rat WAT.
B. Western blottings of extracted proteins from rat WAT. Proteins were separated in 8-16% gradient SDS-PAGE and probed with following cellular protein marker antibodies:
Anti-Na/K ATPase alpha1, a plasma membrane marker (Upstate, clone 464.6), anti-lamin B1, a nuclear envelope marker (ab16048, abcam Cambridge, MA), anti-ubiquinol-cytochrome C reductase core protein (abcam, ab 96333) and GAPDH, a cytosolic marker (Sigma). The specific protein bands were visualized by a substrate Opti-4CN (Bio-RAD).
Kit includes:
|
Items
|
Quantity
|
|
Buffer A (Extraction Buffer)
|
15 ml
|
|
Buffer B (10 X Denaturing Buffer)
|
1.5 ml
|
|
Buffer C (10 X Non-Denaturing Buffer)
|
1.5 ml
|
|
1.5 ml Microfuge Tubes
|
20 units
|
|
Pestles for 1.5 ml Tubes
|
2 units
|
|
Filter Cartridge with Collection Tubes
|
20 units
|
|
Protein Extraction Powder
|
2 grams
|
- Shah, A. P., Johnson, M. D., Fu, X., Boersma, G. J., Shah, M., Wolfgang, M. J., ... & Baraban, J. M. (2019). Deletion of translin (Tsn) induces robust adiposity and hepatic steatosis without impairing glucose tolerance. International Journal of Obesity, 1.
- Li, M., Wang, M., Liu, Y., Huang, S., Yi, X., Yin, C., ... & Xiao, Y. (2019). TNF‐α Upregulates IKKε Expression via the Lin28B/let‐7a Pathway to Induce Catecholamine Resistance in Adipocytes. Obesity.
- Jahandideh, F., de Campos Zani, S. C., Son, M., Proctor, S. D., Davidge, S. T., Chan, C. B., & Wu, J. (2019). Egg white hydrolysate enhances insulin sensitivity in high fat diet induced insulin resistant rats via AKT activation. British Journal of Nutrition, 1-25.
- Zhang, F., Li, D., Wu, Q., Sun, J., Guan, W., Hou, Y., ... & Wang, J. (2019). Prepartum body conditions affect insulin signaling pathways in postpartum adipose tissues in transition dairy cows. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 10(1), 38.
- Wang, N., Ma, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, L., Yang, K., Wei, Y., ... & Wen, D. (2019). Hydroxytyrosol prevents PM2. 5-induced adiposity and insulin resistance by restraining oxidative stress related NF-κB pathway and modulation of gut microbiota in a murine model. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 141, 393-407. Zani, S. (2019).
- Exploratory study of egg white hydrolysate mechanisms of action in insulin sensitive tissues of high fat diet-induced insulin resistant rats. https://doi.org/10.7939/r3-vpcv-w240
- Vianello, E., Dozio, E., Bandera, F., Froldi, M., Micaglio, E., Lamont, J., ... & Schmitz, G. (2020). Correlative study on impaired prostaglandin E2 regulation in EAT and maladaptive cardiac remodeling via EPAC2 and ST2 signaling in overweight CVD subjects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21, 520.
- Fu, X., Shah, A. P., Li, Z., Li, M., Tamashiro, K. L., & Baraban, J. M. (2020). Genetic inactivation of the translin/trax microRNA-degrading enzyme phenocopies the robust adiposity induced by Translin (Tsn) deletion. bioRxiv



